PV SOLAR
Photovoltaic (PV) solar power is increasingly becoming a major source of electricity generation globally. It has become the most popular form of renewable energy generation, surpassing Wind for the first time in 2013. In 2013, new PV solar electricity generating capacity hit record highs in China, Japan and the US, with PV Solar having the second highest total for new electricity generating capacity in the US, after natural gas.
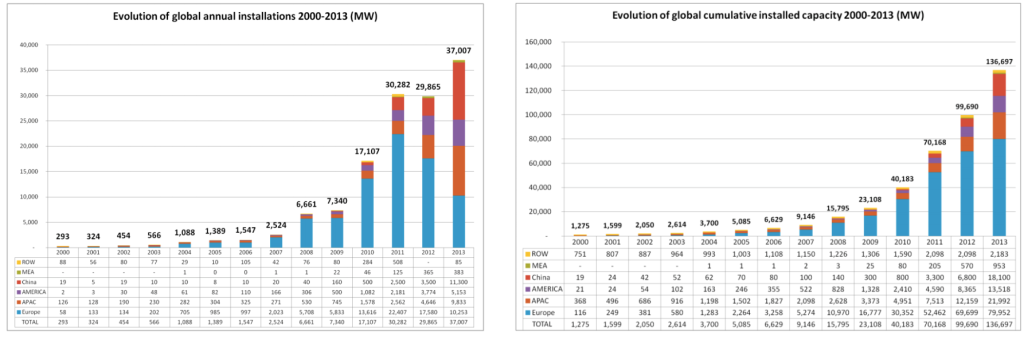
The charts above show the exponential increase in Global PV Solar generation over the past few years.
In some countries, government incentives have favoured the building of ‘solar farms’, often with several hundred MWp each. This has not occurred in Australia, however, where financial incentives have been primarily directed at Distributed, or Rooftop, PV Solar.
Distributed PV Solar, where the electricity is generated on site, usually the roof, and used on site, accounts for the overwhelming majority of PV Solar capacity installed in Australia to date. Initially, the incentives favoured the Residential sector but increasingly Business is seeing the benefits of Distributed PV Solar and the installation of a PV system on its roof, is becoming a standard feature of many businesses’ Energy Cost Minimisation Strategy.
This has been prompted by rapidly rising electricity tariffs and a dramatic fall in the cost of PV systems, resulting in grid-price parity of PV-generated electricity for many Australian businesses. And as these trends continue, the financial benefits of self-generation will only increase and ultimately apply to all businesses.
In addition to the purely financial benefits of self-generation, it also:
- reduces energy price volatility
- increases security of supply
- helps achieve carbon abatement objectives
To date, PV systems have been sized to try and meet a business’ electricity consumption during daylight hours, when PV Solar generates electricity. However, this is often only a fraction of a business’ total electricity consumption over a 24 hour period because there hasn’t been a financially viable method of storing surplus PV generated electricity – until now!
ENERGY STORAGE
Distributed electricity storage, where power is stored on-site by businesses, is becoming an increasingly attractive business proposition.
Although there are various forms of electricity storage, it is the innovation and mass production of batteries for electric vehicles, against the backdrop of rapidly rising electricity tariffs, which has been the catalyst for this development.
By having battery storage capacity, a business can take advantage of the usually major price differential between Peak and Off Peak electricity, allowing it to:
- reduce or even eliminate Peak power charges, by using electricity from batteries charged during the Off Peak tariff period to meet its electricity requirements during Peak tariff periods.
- reduce Peak Load (kVA) network charges by using battery storage power to reduce grid power during regular or intermittent ‘spikes’ in electricity consumption.
- Battery storage also enables the storing of surplus PV electricity, and so for the first time PV systems can be sized to meet Total, not just Daytime, electricity consumption.
ENERGY INDEPENDENCE
PV Solar and Energy Storage can be undertaken as separate, stand-alone Energy Cost Minimization Strategies, but by combining Solar plus Storage, you can minimise your dependence on the large power utilities, possibly achieving ENERGY INDEPENDENCE.
You can:
- Reduce your energy cost, now and into the future
- Reduce your energy cost volatility
- Increase the security of your energy supply
- Reduce your carbon footprint
And best of all, this can be achieved at ZERO COST TO YOU! If you would like to discuss how your business could install Solar plus Storage, and become more energy independent at zero cost to your business, contact Richard Pryke on 0435 628 138 or email: {HERE}

